Introduction to Sustainable Pest Control
Sustainable pest control strategies are essential in minimizing the environmental impact of pest management while maintaining effective control over pest populations. Traditional pest control methods often rely heavily on chemical pesticides, which can lead to environmental contamination, the development of pest resistance, and harm to non-target species. Sustainable strategies aim to reduce these negative effects by integrating environmentally friendly practices that are both effective and safe for the long term.
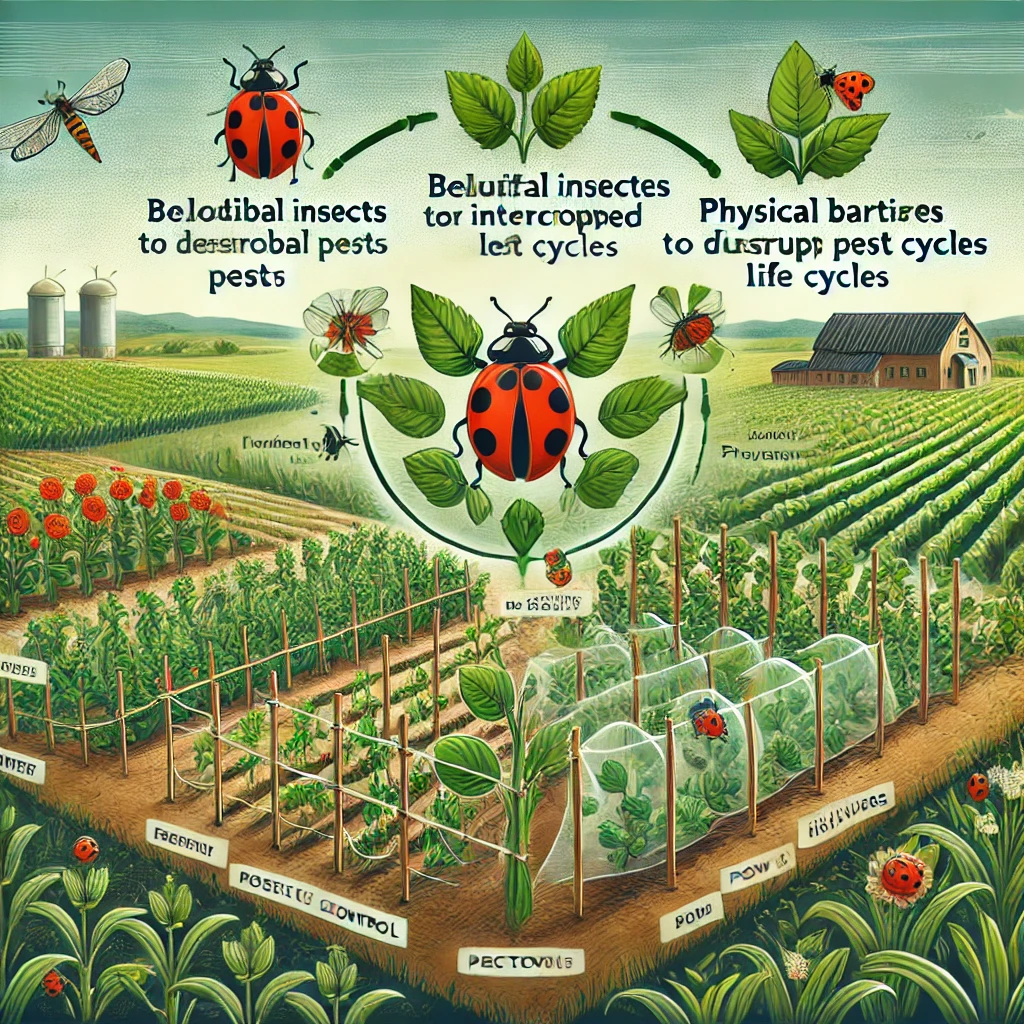
Biological Control Methods
Biological control is a cornerstone of sustainable pest management. This method involves the use of natural predators, parasites, or pathogens to control pest populations. For example, ladybugs are often used to control aphids, while parasitic wasps can be introduced to manage caterpillar infestations. Biological control reduces the need for chemical pesticides and helps maintain the ecological balance by promoting natural pest control mechanisms. This approach is particularly effective in agricultural settings where maintaining soil and plant health is crucial.
Cultural Practices and Crop Management
Cultural practices play a significant role in sustainable pest control by altering the environment to make it less conducive to pest outbreaks. Crop rotation, intercropping, and the use of cover crops are examples of cultural practices that can reduce pest pressure. By rotating crops, farmers can disrupt the life cycles of pests that depend on specific plants, while intercropping can provide a habitat for beneficial insects that prey on pests. These practices not only help in controlling pests but also improve soil health and crop productivity.
Mechanical and Physical Controls
Mechanical and physical controls are sustainable methods that involve the use of barriers, traps, and other physical means to prevent or reduce pest infestations. Examples include using row covers to protect crops from insect pests, setting up traps for rodents, and installing barriers to prevent pest entry into buildings. These methods are effective in reducing pest populations without the need for chemical interventions. They are often used in conjunction with other sustainable practices to create an integrated pest management (IPM) approach.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach that combines multiple sustainable strategies to manage pest populations effectively. IPM involves regular monitoring of pest levels, identifying the most appropriate control methods, and using a combination of biological, cultural, mechanical, and, when necessary, chemical controls. The goal of IPM is to minimize the use of harmful chemicals, reduce the risk of pest resistance, and protect the environment while maintaining effective pest control. IPM is widely recognized as the most effective and sustainable approach to pest management.
